- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Small Volume Injections›
- Dexamethasone Injection
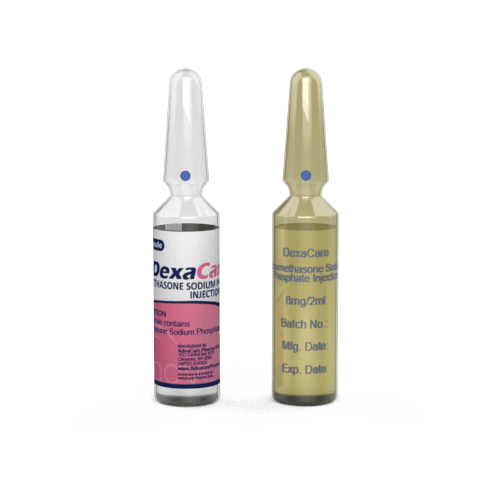
Dexamethasone Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Dexamethasone?
Active Ingredients: Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone Injection is a drug used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. It is commonly used in the treatment of conditions like arthritis, certain cancers, ophthalmologic diseases, intestinal disorders, breathing problems, adrenal gland problems, swelling, and skin disease.
Injections of dexamethasone are also used to prevent and treat chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. It is also used as a diagnostic tool for testing for Cushing's syndrome.
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid belonging to a class of drugs known as corticosteroids. This drug works to decrease the immune system's response, which reduces symptoms like itching, swelling, redness, and allergic reactions.
AdvaCare Pharma produces dexamethasone in a wide range of forms, including oral medicines such as Dexamethasone Tablets. Dexamethasone Eye Drops are also available for distribution.
AdvaCare Pharma is a GMP-certified producer and supplier of Dexamethasone Injections. This medication is manufactured in our factories in China, India, and the USA. Our production facilities are regularly inspected to ensure our products meet quality and safety standards.
Why are we a leading Dexamethasone manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma, a US-owned pharmaceutical company, is a manufacturer of Dexamethasone Injection with GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities located worldwide. We conduct frequent GMP, third-party and internal facility inspections to ensure that our manufactured injectable treatments exceed the stringent requirements of importing countries and our distributors.
As a renown Dexamethasone manufacturer and global supplier of 120+ pharmaceutical injection products, our global reach extends to over 65 markets ensuring that pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs and government institutions receive the quality-assured treatments they need.
Uses
What is Dexamethasone used for?
It is used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. It is indicated for the treatment of a wide range of conditions, including:
- inflammatory conditions
- certain cancers, such as multiple myeloma
- intestinal disorders
- breathing problems, such as acute asthma
- adrenal gland problems
- acute mountain sickness
- cerebral edema
- shock
- laryngotracheobronchitis (childhood croup)
- skin diseases and lesions
Dexamethasone Injection is also used as a diagnostic tool for Cushing's syndrome. The dexamethasone suppression test is typically conducted if a patient is thought to be producing too much cortisol in order to help identify if the cause of the problem is with the pituitary gland or another site in the body.
How are Dexamethasone Injections used?
This medication is manufactured as a solution. It is intended to be administered by a healthcare professional in a hospital or clinic setting. Dexamethasone Injections should be given by injection into a vein, muscle, joint, or skin, as indicated by a doctor.
How should Dexamethasone Injections be stored?
This medicine should be stored in its original packaging until use. It is recommended to keep the product in a location that is protected from light. Do not freeze or refrigerate the solution.
What dose should be given?
Adult Dosing Recommended dosage may vary based on different medical conditions:
- For inflammation, the usual dose for adults is 0.5-9mg per day, given in divided doses every 6-24 hours by IV or IM.
- For cerebral edema, the usual dose is 10mg by IV followed by 4mg given by IM every 6 hours until clinical improvement. After 2-4 days, dosage may be reduced and then gradually discontinued over 5-7 days.
- For shock, the usual dose is 1-6mg/kg, given once IV. Alternatively, 40mg can be administered IV every 2-6 hours, as needed. Alternatively, 20mg can be given IV, followed by 3mg/kg per day, given by continuous IV infusion. It should be noted that high-dose treatments should be discontinued after 48-72 hours.
- For severe allergic conditions unresponsive to other treatments, the usual dose is 4-8mg given IM, followed by oral therapy.
- For COVID-19 in patients undergoing invasive mechanical ventilation or oxygen alone, the usual dose is 6mg IV per day for up to 10 days. Treatment is not recommended for hospitalized patients, not for respiratory support.
- For chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, the usual dose is 8-12mg IV, either administered alone or with other antiemetics before chemotherapy. After chemotherapy, 8mg IV can be administered every 24 hours for 1-3 days (days 2-4).
- For acute mountain sickness, the usual dose is 4mg, given IV or IM, every 6 hours. For high-altitude cerebral edema, 8mg can be administered, followed by 4mg every 6 hours until the resolution of symptoms.
- For malignant spinal cord compression (off-label), the usual dose is 10-100mg given IV. Treatment should begin when neurological symptoms appear. 4-24mg can be administered during radiation therapy, and dosage should be tapered when discontinuing.
Pediatric Dosing Recommended dosage for children may vary based on different medical conditions:
- For airway edema, the usual dose is 0.5-2mg/kg per day, given IV or IM. The dosage should be divided and given every 6 hours, beginning 24 hours before extubation. Treatment should continue for 4-6 days afterward.
- For childhood croup, the usual dose is 0.6mg/kg, given once IV or IM. The maximum dosage is 16mg.
- For inflammation, the usual dose is 0.08-0.3mg/kg per day, given IV or IM. The dosage should be divided and given every 6 or 12 hours.
- For meningitis in children over 6 weeks old, the usual dose is 0.6mg/kg per day, divided and given IV every 6 hours for the first 2-4 days. The first dose should start 10-20 minutes before or at the same time as the first antibiotic dose.
- For cerebral edema associated with brain tumors, the usual dose is 1-2mg/kg, given once IV/IM. For maintenance therapy, the usual dose is 1-1.5mg/kg per day, which should be divided and given every 5-6 hours IV/IM. The maximum dosage is 16mg per day.
- For spinal cord compression, the usual dose is 2mg/kg per day, divided and given every 6 hours IV.
- For prophylaxis for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) in premature infants, the usual dose is 4mg IM administered to the mother every 8 hours, beginning 2 days before delivery.
The dosage is based on medical condition, response to the treatment, age, and weight. Refer to a doctor or pharmacist for guidelines on the exact dosage according to a medical condition.
Who can use Dexamethasone?
Dexamethasone Injection can be administered to adults and children, but caution is advised for specific groups of patients.
Pregnant Benefits must be weighed against the risks when being administered to pregnant women, particularly during the 1st trimester or with any long-term treatments. It is known that corticosteroids cross the placenta. Limited human data suggests the possibility of adverse developmental outcomes, such as the risk of low birth weight, premature birth, or orofacial cleft. Due to dexamethasone's mechanism of action, there is a possible risk of fetal adrenal suppression.
Breastfeeding Women should avoid breastfeeding during treatment and for 2 weeks after the last dose of dexamethasone. When administered systemically, corticosteroids are excreted in milk and may interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production and suppress growth.
Children Ongoing treatment with corticosteroids is associated with inhibiting bone growth and overall velocity growth in pediatric patients. Children should be regularly monitored while being treated with this medicine.
Geriatric Corticosteroids are associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis, so special considerations may be needed for patients, such as postmenopausal women and the elderly, with a higher risk of developing osteoporosis. Bone mineral density should be monitored during long-term treatment in patients over the age of 65 years old.
Other warnings
During treatment with dexamethasone, healthcare providers should consider monitoring electrolytes, blood pressure, weight, and postprandial glucose (2h).
During long-term treatment, some patients may need chest X-rays, or ophthalmic exams to assess any potential side effects.
For patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease or severe dyspepsia, an upper GI x-ray may be recommended to evaluate any complications.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Dexamethasone Injection.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- upset stomach
- dizziness
- headache
- menstrual period changes
- insomnia
- increased appetite
- diarrhea
- constipation
- vomiting
- weight gain
- swelling or pain near the injection site
Serious side effects may include:
- signs of an allergic reaction
- changes in behavior or mood
- changes in vision
- rapid weight gain or unusual swelling
- signs of stomach bleeding
- seizures
- signs of low potassium levels
- pancreatitis
- changes in heart rate
Long-term treatment with dexamethasone is associated with the following adverse effects:
- osteoporosis
- glaucoma
- cataracts
- immunosuppression
- Kaposi sarcoma
- withdrawal symptoms with abrupt discontinuation
- growth suppression in children
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or you notice any other symptoms, please call your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Dexamethasone Injection if:
- You are allergic or hypersensitive to any of the ingredients.
- You have a systemic fungal infection.
- You have cerebral malaria or ocular herpes infection.
Before treatment, consult your doctor regarding any medications you are taking to address potential drug interactions.Some known interactions include apixaban, lumefantrine, certain antipsychotics (cariprazine, lurasidone), NSAIDs, antivirals, hormone medications (e.g. certain birth control pills), naloxegol, praziquantel, cobimetinib, regorafenib, and vandetanib. This is not a complete list of possible interactions. Dexamethasone is contraindicated with live vaccines, desmopressin, mifepristone, and rilpivirine.
This medication may not be suitable for people with certain conditions, so it is important to consult with a doctor if you have any health conditions. Some conditions that may need additional considerations include tuberculosis, cirrhosis or other liver diseases, malaria, osteoporosis, glaucoma, cataracts, ulcerative colitis, depression or any other mental illness, a recent heart attack, congestive heart failure, herpes, an eye infection, or high blood pressure.
References
Comparative efficacy and safety of different corticosteroids to reduce inflammatory complications after mandibular third molar surgery: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
This meta-analysis was performed to assess the comparative effectiveness of corticosteroids in reducing inflammatory complications after a mandibular third molar surgery. The research was done through various databases and only randomised clinical trials were included.
The authors found 2427 results, and 61 studies involving 3561 subjects met the inclusion criteria. Five corticosteroids were compared including dexamethasone, betamethasone, methylprednisolone, prednisolone, and triamcinolone. Both dexamethasone at a dosage of 8mg via submucosal injection (-3.58[-6.98; -0.17]) and via pterygomandibular injection (-3.56[-6.30; -0.82]) were more effective than placebo in reducing edema after third molar surgery (3MS).
The ranking analysis suggested that dexamethasone 8mg via submucosal injection and oral tablets had the highest likelihood of being the most effective interventions for reducing edema after 3MS (p values = 0.71 and 0.75, respectively). Dexamethasone 8mg via submucosal injection was the only treatment that effectively reduced pain on the first and second days after 3MS compared to placebo (-30.95[-43.41; -18.49] and -15.25[-23.27; -7.22], respectively).
The conclusion of this study is that dexamethasone is the preferred preoperative option for managing inflammatory complications after 3MS.
You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.