- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Small Volume Injections›
- Promethazine Injection
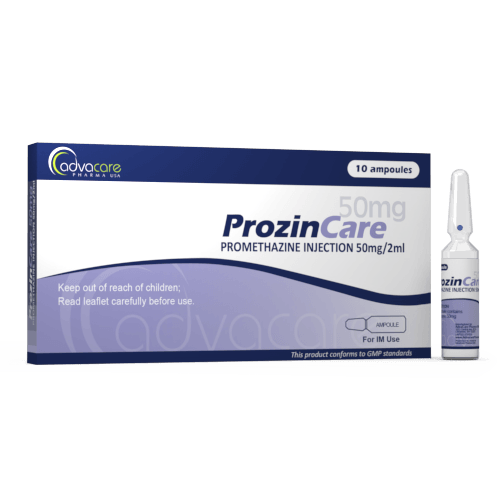
Promethazine Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Promethazine?
Active Ingredients: Promethazine
Promethazine Injection is an antihistamine, antiemetic, analgesic, and anticholinergic medication with CNS depressant effects. It is used in the treatment of allergic reactions, to control nausea and vomiting associated with operations or motion sickness, and as a sedative before, during, and after surgery.
Promethazine is a derivative of phenothiazine that was approved by the FDA by 1951. It is a first-generation antihistamine that acts as a histamine H1 receptor antagonist by preventing histamine from binding to its receptor. Promethazine is also an antagonist of dopamine D2, adrenergic, muscarinic, and NMDA receptors.
Promethazine’s antagonism of muscarinic and NMDA receptors contributes to its parasympathetic nervous system sedation effects and its antagonism of histamine H1, medullary dopamine, and muscarinic receptors supports the prevention of nausea and vomiting.
As an antihistamine, promethazine is used in adjunct with epinephrine to treat anaphylaxis and prophylactically to prevent certain allergic reactions, such as allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, urticaria, and angioedema.
As an antiemetic, promethazine is used to control nausea and vomiting associated with operations, motion sickness, chemotherapy, or other causes.
As a sedative, promethazine can be used as a sedative in adjunct with other analgesics before, during, or after medical procedures or childbirth. It can be administered to improve the efficiency of some opioids, such as meperidine.
Injections of promethazine are typically given when a patient is unable to take this medication orally as a syrup or tablet.
AdvaCare is a GMP manufacturer of Promethazine Injections. This medication is produced in our factories in China, India, and the USA. We routinely inspect our production facilities to ensure our products meet quality and safety standards.
Why are we a leading Promethazine manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma, a US-owned pharmaceutical company, is a manufacturer of Promethazine Injection with GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities located worldwide. We conduct frequent GMP, third-party and internal facility inspections to ensure that our manufactured injectable treatments exceed the stringent requirements of importing countries and our distributors.
As a renown Promethazine manufacturer and global supplier of 120+ pharmaceutical injection products, our global reach extends to over 65 markets ensuring that pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs and government institutions receive the quality-assured treatments they need.
Uses
What is Promethazine used for?
Promethazine is intended for the following uses:
- Alleviate allergic reactions to blood or plasma.
- During anaphylaxis as an adjunct to epinephrine after acute symptoms have been controlled.
- Treat mild hives or swelling from allergic reaction, when oral therapy is unavailable.
- Treat motion sickness.
- Prevent and control nausea and vomiting associated with certain types of anesthesia and surgery.
- Sedation, relief of apprehension, and producing a light sleep from which a patient can be easily aroused.
- As an adjunct to analgesics for the management of postoperative pain.
- Preoperative, postoperative, and obstetric sedation.
How are Promethazine Injections used?
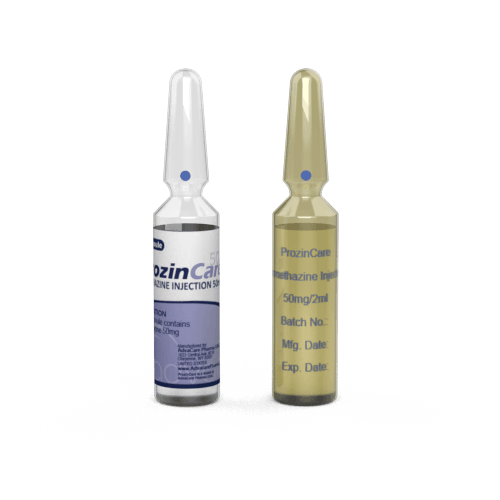
This medication is manufactured as a clear, colorless solution. Each milliliter of solution contains 25mg of promethazine. It is intended to be administered by intravenous (IV) or deep intramuscular (IM) injection by a healthcare professional in a hospital or clinic setting.
Promethazine Injection is contraindicated for subcutaneous or intra-arterial administration due to the risk of tissue damage. IV use should be performed with caution as severe tissue damage may also occur. Promethazine may be diluted before IV administration to prevent promethazine-induced tissue necrosis.
When giving a Promethazine Injection, it is especially important to monitor cardiac function, potassium concentration, and acid-base balance. It should not be infused rapidly to avoid potassium intoxication. Do not use other potassium-containing salt substitutes when using potassium chloride injection.
What dose should be given?
The usual dose for adults and children is dependent on the intended use and the patient’s weight:
- It is recommended to not exceed 10mEQ/hour or 200mEQ/day if the patient's potassium level is greater than 2.5mEQ/liter.
- For treatment of nausea and vomiting in children, the recommended dose is 0.5mg/lb of bodyweight. The dose should also be based on the child’s age and the severity of nausea/vomiting. As a preoperative medication in adjunct with another analgesic, the recommended dose for children is 0.5mg/lb.
- Postoperative sedation and adjunctive use with analgesic medicines may be achieved by 12.5mg to 25mg in children. The dosage for children ≥ 2 years should not exceed half the recommended adult dose.
- For the prophylaxis of nausea and vomiting during surgery and postoperatively in adults, the recommended dose is 25mg administered at four to six-hour intervals. To produce a quiet sleep or sedation and relieve apprehension prior to surgery or childbirth, the recommended dose for adults is between 25mg to 50mg. Postoperative sedation and adjunctive use with analgesic medicines may be achieved by 25mg to 50mg in adults.
Promethazine may intensify, increase, or prolong the sedative action of other CNS depressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants, narcotics, alcohol, general anesthetics. Patients who take these medicines should avoid promethazine or receive a lower dosage. When promethazine is concomitantly administered, the dose of barbiturates should be reduced by at least 50%, and narcotics by 25% to 50%.
Refer to a doctor or pharmacist for guidelines on the exact dosage.
How often can Promethazine be given?
The effects of promethazine can last from four to six hours.
Repeated doses should not exceed six times a day, or every four hours:
- When treating allergic reactions, the average adult dose (25mg) can be repeated within two hours, if necessary. After treatment initiation, dosage should be adjusted to the minimal dosage that can relieve symptoms.
- When treating nausea and vomiting, doses can be given every four hours.
- For concomitant use with analgesics as a sedative during childbirth, after the initial dose, one or two more doses can be given in four-hour intervals. In a 24-hour period, a maximum dose of 100mg may be administered to patients in labor.
Promethazine is a prescription-only controlled-substance that has the potential for abuse and is not recommended for long-term use. Use this medication only as directed by a doctor or other licensed healthcare provider.
Who can use Promethazine?
Promethazine can be administered to adults and children, but caution is advised for specific groups of patients.
Pregnant Promethazine is a category C pregnancy risk. Risk of teratogenic effects cannot be ruled out; Animal studies have shown potential risk to fetus, but there are no adequate studies on pregnant humans.
Promethazine Injection should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benefit justifies any potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing It is unknown whether promethazine is excreted in human milk, but many drugs are. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, either nursing or promethazine should be discontinued, based on the importance of the drug to the patient.
Pediatric In pediatric patients < 2 years old, Promethazine Injection use is contraindicated because of the risk of fatal respiratory depression.
In pediatric patients ≥ 2 years old:
- Promethazine Injection use should be avoided in patients currently taking respiratory depressants or experiencing signs and symptoms of Reye’s syndrome or other hepatic disease.
- Promethazine Injection use is not recommended for children with vomiting of unknown etiology, acute illness or dehydration, asthma, liver disease, seizure disorders, or glaucoma.
- Promethazine Injection should be used with caution in pediatric patients who have a history of sleep apnea, family history of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), or are less prone to spontaneous arousal from sleep.
Geriatric There are insufficient studies on adults ≥ 65 years old to determine whether they respond differently than adults < 65 years old.
Due to promethazine’s increased risk of sedative effects and confusion, dosing in geriatric patients should be reduced and done with caution because of age-related decreases in hepatic, renal, and/or cardiac function and concomitant disease and drug therapy. Close observation is recommended.
Due to some of promethazine’s potential anticholinergic side effects, such as blurred vision, dry mouth (xerostomia), dry nasal passages (atrophic rhinitis), dilated pupils, constipation, and urinary retention, the American Geriatrics Society categorizes Promethazine as a potentially inappropriate drug for older patients.
Other contraindications
Promethazine Injection should be used with caution in adults with seizure disorders or who are taking medications that may lower the seizure threshold (i.e., local anesthetics) and patients with bone marrow depression.
Promethazine use alone or in combination with other antipsychotic drugs could result in the development of a potentially fatal neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS). Clinical symptoms of NMS are hyperpyrexia, altered mental status, muscle rigidity, diaphoresis, irregular heartbeats or blood pressure, tachycardia, and cardiac dysrhythmias.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Promethazine Injection.
Common side effects include, but are not limited to:
- dizziness
- drowsiness
- restlessness
- swelling near the injection site
Serious side effects may include:
- signs of an allergic reaction
- tissue damage near the injection site
- seizures
- cardiovascular changes (arrhythmias and hypotension)
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or you notice any other potential symptoms not listed, please contact your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Promethazine Injection if:
- You are allergic to promethazine or any of the other ingredients.
- You are allergic to local anesthetics with ester groups, such as cocaine, procaine, benzocaine, or para-substituted groups in parahydroxybenzoate.
Promethazine Injections should not be administered to children < 2 years old because of the risk of fatal respiratory depression.
This drug can also affect potassium levels, so it is important to monitor potassium levels when using this medication.
References
Intravenous promethazine versus lorazepam for the treatment of peripheral vertigo in the emergency department: A double blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety
The main objective of this research was to assess whether promethazine has superior vertigo reduction compared with lorazepam in ED patients.
This is a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial; 184 patients were assigned (1:1 ratio) to receive either promethazine, 25mg intravenously, or lorazepam, 2mg intravenously.
The primary endpoint assessed the mean alteration in vertigo intensity at the 2-hour mark using the visual analog scale (VAS). Secondary endpoints included evaluating the mean change in nausea score, the necessity for a second dose of study medications, and monitoring adverse events (AEs). The findings revealed that promethazine led to a significantly greater reduction in vertigo intensity (46.5mm) compared to lorazepam (25.7mm, p < 0.001). The mean change in nausea score 2 hours post-drug administration, as measured on the VAS, was 28.7mm for promethazine and 22.8mm for lorazepam (p=0.002). Lethargy was the most commonly reported AE, occurring in 14.1% of the lorazepam group and 4.3% of the promethazine group (p=0.013), while drowsiness was reported in 10.8% of the promethazine group and 2.1% of the lorazepam group (p=0.017).
The findings indicate that promethazine is superior to lorazepam in the management of peripheral vertigo and vertigo-related nausea in ED adults.
You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.