- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Small Volume Injections›
- Sodium Bicarbonate Injection
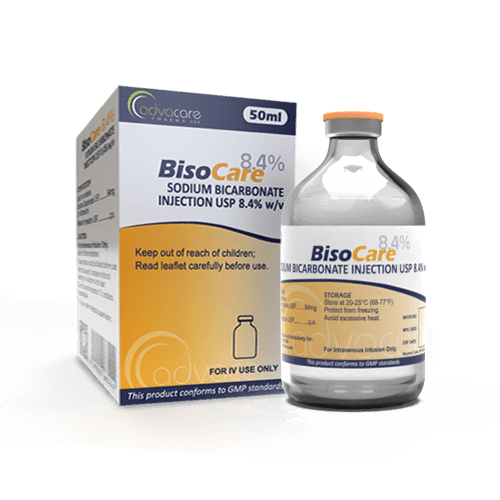
Sodium Bicarbonate Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Sodium Bicarbonate?
Active Ingredients: Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium Bicarbonate Injections are used to treat metabolic acidosis caused by severe renal disease, severe primary lactic acidosis, uncontrolled diabetes, or cardiac arrest. It is also used to treat this condition when caused by circulatory insufficiencies due to shock or severe dehydration.
This medication is indicated for the treatment of cardiac conduction delays and QRS prolongation.
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) is a compound composed of sodium and bicarbonate, which is used as an alkalinizing agent. It works by buffering excess hydrogen ion concentration within the blood. By raising blood pH, sodium bicarbonate helps reverse the clinical manifestations of acidosis.
This medication is an aqueous, sterile, nonpyrogenic, and hypertonic solution of sodium bicarbonate. The solution does not contain bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent, or added buffer.
Sodium Bicarbonate Injections are produced in two formulations, 4.2% and 8.4%, and they are available packaged as ampoules or a 50mL vial of solution.
Sodium Bicarbonate Tablets are also available for distribution.
AdvaCare Pharma is a trusted global exporter of Sodium Bicarbonate Injections. This medication is produced in our GMP-certified facilities in China, India, and the USA. Our manufacturing facilities are regularly inspected to ensure they comply with WHO's standards, rules, and regulations.
Why are we a leading Sodium Bicarbonate manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma, a US-owned pharmaceutical company, is a manufacturer of Sodium Bicarbonate Injection with GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities located worldwide. We conduct frequent GMP, third-party and internal facility inspections to ensure that our manufactured injectable treatments exceed the stringent requirements of importing countries and our distributors.
As a renown Sodium Bicarbonate manufacturer and global supplier of 120+ pharmaceutical injection products, our global reach extends to over 65 markets ensuring that pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs and government institutions receive the quality-assured treatments they need.
Uses
What is Sodium Bicarbonate used for?
It is used to treat metabolic acidosis (too much acid in the blood) that may be caused by conditions such as:
- cardiac arrest
- circulatory problems due to severe dehydration or shock
- drug or alcohol toxicities, including barbiturates, salicylates, and methyl alcohol
- extracorporeal circulation of blood
- severe primary lactic acidosis
- severe renal disease
- uncontrolled diabetes
- severe diarrhea with bicarbonate loss
It is also used to treat cardiac conduction delays and QRS prolongation.
What is the difference between Sodium Bicarbonate Injections and Sodium Bicarbonate Tablets?
These two forms of sodium bicarbonate serve different clinical purposes. Oral administration of sodium bicarbonate is typically used to treat mild gastrointestinal issues, while injections are used for medical conditions or emergencies requiring precise dosing and rapid intervention.
How are Sodium Bicarbonate Injections used?
This medication is manufactured as a solution intended for intravenous administration. It is typically given by a healthcare professional in a hospital or clinic setting.
Before administration, the solution should be carefully examined for any signs of visible particles or discoloration. Any compromised solutions should be thrown out.
It should be noted that Sodium Bicarbonate Injections in ampoules or vials are intended for single use. If a smaller dose is used, any unused portion of the solution should be discarded.
How should Sodium Bicarbonate Injections be stored?
It is advised to store this medication in its original packaging until use. This product should be stored at room temperature (between 20-25°C). Do not freeze the solution. Keep any unused vials or ampoules out of excessive heat above 40°C, though brief exposures to temperatures up to 40°C should not adversely affect the integrity of this medicine.
What dose should be given?
Adult Dosing Dosage may vary based on different medical indications:
- For acute metabolic acidosis (non-threatening), the usual dose is 2-6mEq/kg given by IV. Subsequent doses are based on the patient’s response to the injection and acid-base status. For mild acidosis, the usual dose is 1-2mEq/kg.
- For severe metabolic acidosis (not including hypercarbic acidosis), the usual dose is 90-180 mEq/L, given at a rate of 1-1.5L for the first hour.
- For cardiac arrest, the usual dose is 44.6-100 mEq (1-2 vials of 50mL) given by rapid IV, followed by a rate of 34.6-50mEq every 5-10 minutes, if necessary. After the initial treatment, further doses are dependent on the arterial blood pH and PaO2.
- For hyperkalemia, the usual dose is 50mEq, given over 5 minutes IV.
- For salicylate overdose in patients with a urinary pH <7.5, the usual dose is 1-2mEq/kg per dose IV. Subsequent doses are determined by the patient’s response to the injection and urinary pH.
- For tricyclic antidepressant overdose in patients with QRS > 100ms or serum pH <7.45, the usual dose is 1-2 mEq/kg per dose IV. Subsequent doses are based on the patient’s response to the injection and serum pH. Subsequent doses are based on the patient’s response to the injection and acid-base status.
Pediatric Dosing Recommended dosage for children may vary based on different medical conditions:
- For acute metabolic acidosis (non-life-threatening), the usual dose (mEq) = 0.3 x weight (kg) x base deficit (mEq/L). Alternatively, the individualized dose can be calculated by dose (mEq) = 0.5 x weight (kg) x (24-serum HCO3 (mEq/L)). For older children, the dose is typically 2-5mEq/kg, administered over 4-8 hours by IV infusion.
- For cardiac arrest in infants and children under 2 years old, the usual dose is 1mEq/kg per min, administered over 1-2 minutes IV/IO, followed by 1mEq/kg IV, given every 10 minutes of continued cardiac arrest. The maximum dosage is 8mEq/kg per day.
- For cardiac arrest in children over 2 years old, the usual dose is 1mEq/kg per min, administered over 1-2 minutes IV. Subsequent doses are determined by the patient’s arterial blood pH and PaCO2. For prolonged cardiac arrest, additional doses may be considered only after adequate alveolar ventilation.
The exact dosage is based on medical condition, response to the treatment, age, and weight. Refer to a doctor or healthcare professional for guidelines on dosage.
Who can use Sodium Bicarbonate?
Sodium Bicarbonate Injections can be administered to adults and children, but caution is advised for specific groups of patients.
Pregnant Sodium bicarbonate should only be administered to pregnant women if there is a clear need and the benefits must be weighed against the risks. Due to the drug’s mechanism of action, there is a possible risk of fluid retention. There are inadequate human and animal data available to assess the risk of fetal harm or the effect on reproduction capacity.
Breastfeeding The benefits must be weighed against the risks before administering sodium bicarbonate to breastfeeding women. There is no human data available to properly assess the effects on milk production or the risk of infant harm.
Children In neonates and pediatric patients under 2 years old, rapid injections of sodium bicarbonate 8.4% at a rate of 10mL/min have been associated with hypernatremia. For these patients, the rate of administration should not exceed 8mEq/kg per day, and slow administration of the 4.2% solution is preferable. It should be noted that in emergency situations, (e.g. cardiac arrest), the benefits of rapid infusion must be weighed against the associated risks (e.g. fatality, acidosis).
Geriatric Though there are no known associated risks for elderly patients, it is recommended to use a starting dose at the lower end of the range.
Other warnings
For patients with severe renal disease, congestive heart failure, edema, oliguria, or anuria, large doses of this medicine should be given with caution, due to sodium retention associated with the sodium content of sodium bicarbonate.
Parenteral treatment with any sodium ion medication should be cautiously administered in patients also being treated with corticosteroids or corticotropin.
Extravasation of this medicine has been known to cause necrosis, ischemia, and tissue death. Special care must be taken to avoid errors in administration.
Rapid administration may cause increased intravascular fluid volume. It should be noted that rapid infusion or large doses of sodium bicarbonate may result in acute metabolic alkalosis, which may result in tetany. Therefore, it is recommended to administer sodium bicarbonate at a safe rate, typically 1-2 milliequivalents (mEq) per kilogram (kg) of body weight over 5-10 minutes, to mitigate the risk of adverse effects.
Parenteral administration may cause fluid or solute overloading, which could result in diluted serum electrolyte concentration.
It is recommended that medical staff periodically monitor serum electrolytes, urinary pH, and arterial blood gases (when applicable).
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Sodium Bicarbonate Injection.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- ulcers
- pain or discomfort at the injection site
- edema
- muscle pain
Serious side effects may include:
- signs of an allergic reaction
- metabolic alkalosis
- seizures
- tetany
- necrosis (tissue damage) due to extravasation
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or you notice any other symptoms, please call your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Sodium Bicarbonate Injection if:
- You are allergic to any of the ingredients.
- You are vomiting or have continuous gastrointestinal suction, which has resulted in chloride loss.
- You are undergoing treatment with diuretics.
Due to possible drug interactions, consult with your doctor about any medications, supplements, or herbal products that you are taking before your treatment. Some drugs that are known to interact with this medicine include antibiotics, NSAIDs (e.g. naproxen), corticosteroids, corticotropin, and diuretics.
This medication may not be suitable for people with certain conditions, so it is important to consult with a doctor if you have any health conditions. Special considerations, laboratory tests, or additional monitoring may be necessary for conditions such as breathing or blood abnormalities, dehydration, eclampsia, hypertension (high blood pressure), renal insufficiencies, or heart problems.
Some additives may be incompatible with Sodium Bicarbonate Injection. Norepinephrine and dobutamine are incompatible with this medication.
Avoid using sodium bicarbonate with calcium-containing parenteral solutions, as precipitation may occur.
References
Sodium bicarbonate on severe metabolic acidosis during prolonged cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study
The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of sodium bicarbonate administration in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) patients with severe metabolic acidosis during prolonged CPR.
This is a prospective, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial at a single center emergency department (ED). Following 10 minutes of CPR, patients who did not achieve return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) and presented with severe metabolic acidosis (defined as pH < 7.1 or bicarbonate < 10mEq/L) were included in the study. They were randomly assigned to receive either sodium bicarbonate (n=25) or normal saline (n=25). The primary endpoint assessed was sustained ROSC. Secondary endpoints included evaluating the change in acidosis and determining good neurological survival.
The sodium bicarbonate group demonstrated a big impact on pH (6.99 vs. 6.90, p=0.038) and bicarbonate levels (21.0 vs. 8.0mEq/L, p=0.007), but there were no significant differences observed between the sodium bicarbonate and placebo groups in terms of sustained return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) (4.0% vs. 16.0%, p=0.349) or favorable neurological outcomes at 1 month (0.0% vs. 4.0%, p=1.000).
The findings indicate that sodium bicarbonate improved acid-base status, but did not improve the rate of ROSC and good neurologic survival.
You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.